news
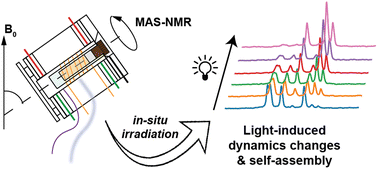
Publication: In-situ irradiated MAS NMR to probe dynamic transitions.
We are excited to report the publication of our paper on in-situ illumination during MAS NMR in the Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This publication is the culmination of a long project that found its origins quite a few years ago, even before the lab moved from Pittsburgh to Groningen. Photochemistry and optogenetics are increasingly influential topics in both chemical and biological research, respectively. The application of illumination and light triggers can be used to control chemical and biological processes. In this paper we focus on the intersection of such processes and materials science – demonstrating how magic-angle-spinning (MAS) NMR […]

New Publication: Silk-inspired hybrid materials – ssNMR and more.
Congratulations to PhD student Raffaella Parlato, as well as our collaborators from the group of Marleen Kamperman, with the publication of a new collaborative paper in the journal Communications Chemistry. Raffaella used solid-state NMR to study the structure and dynamics of (labeled) polypeptides within the hybrid polymer-peptide materials prepared by the Kamperman group. The employed peptides are poly-alanine peptides inspired by the structural motifs found in proteins in spider silk. Spider silk proteins use polyalanine segments to form stable higher order structures that enable the remarkable materials properties of silk. Here, these peptides were used to change the materials properties […]
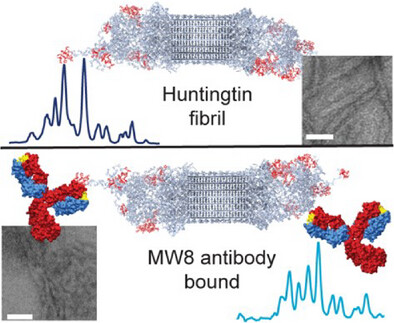
Publication: how antibodies bind to the fuzzy coat of Huntingtin protein fibrils.
Congratulations to Raffaella for the publication of her second first-author paper, this time on the use of NMR spectroscopy to study how antibodies bind to the aggregated state of huntingtin protein fragments, relevant to Huntington’s disease. This work is part of our ongoing research on the biochemistry of Huntington’s disease, and was supported by funds from the European Huntington Disease Network EHDN and the CampagneTeam Huntington. Antibodies are widely used as diagnostic tools in HD research, and also are considered as potential treatment modalities. An example of the latter approach can be found in the case of Alzheimer’s disease, where […]

Publication: Impact of aggregation inhibitors on protein aggregation and aggregate toxicity.
Congratulations to Greeshma Jain, Marina Trombetta-Lima and the whole team of co-authors for the publication of our most recent paper on Huntington’s disease (HD), in the journal Nature Communications. This paper is actually the fourteenth peer-reviewed publication from the lab on HD research, since our first paper in 2011. It was enabled by crucial funding from the CampagneTeam Huntington foundation, who supported our HD research program when the Van der Wel group moved back to the Netherlands. In this new report we describe our use of structural analysis (NMR and EM) to look how aggregation-inhibiting small molecules (polyphenols) change the […]
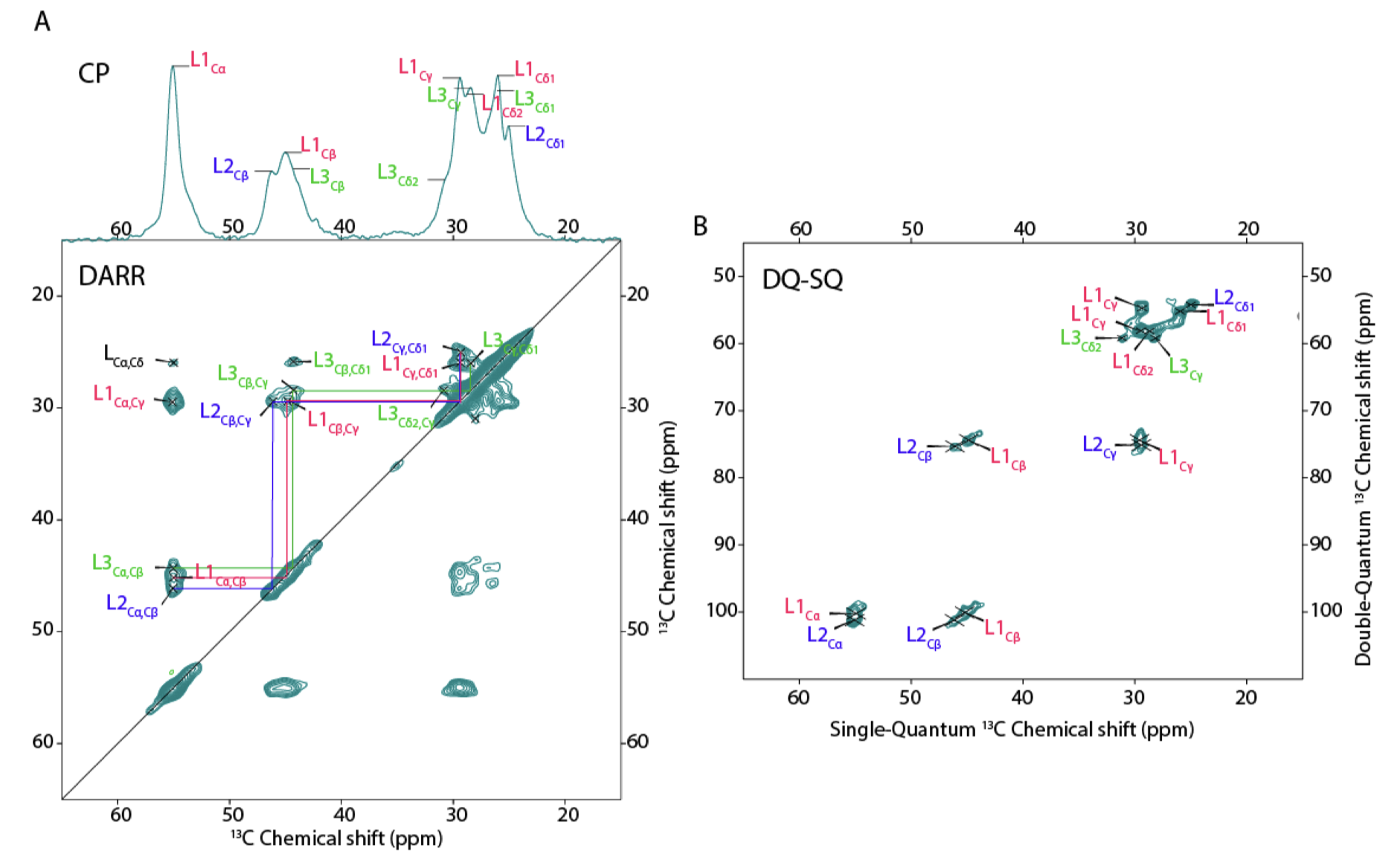
Publication: Peptide-based self-assemblers and self-replicators (with insights from ssNMR).
Congratulations to our collaborators in the group of Sijbren Otto (RUG), and Alessia, for the new paper in the journal Chem. This report discusses how self-assembling and self-replicating molecules can borrow principles from polypeptide amyloid formation. In particular, the concept of ‘steric zippers’ proves to be highly relevant – an idea from the amyloid field that comes out of seminal work by the group of David Eisenberg (UCLA). Our contributions in this new paper relate to the use of 1D and 2D solid-state NMR analysis of the self-assembled materials, in samples where targeted isotope-labeled amino acids were incorporated. With these […]
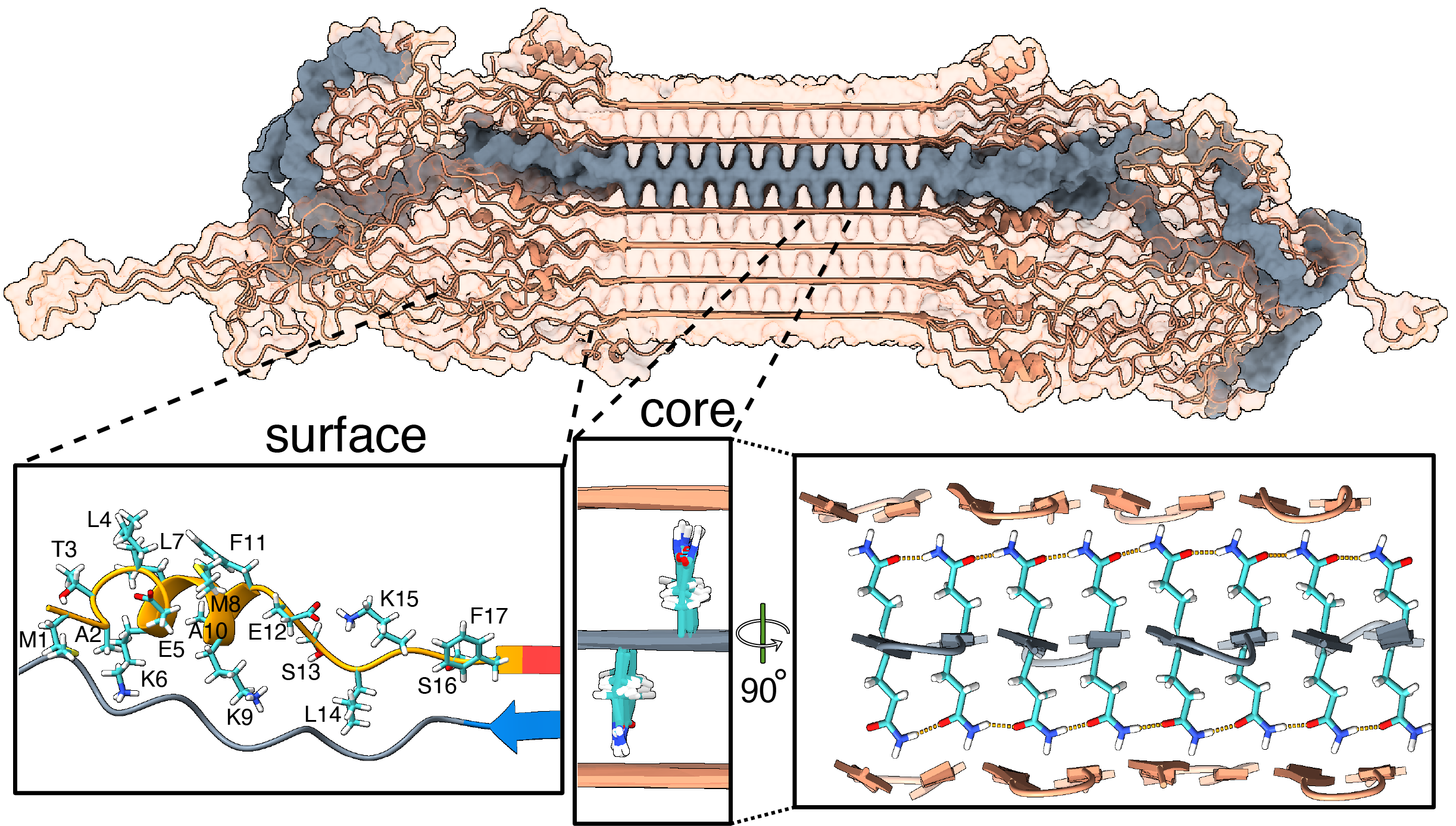
Publication: Structure of protein aggregates implicated in Huntington disease
Congratulations to Irina, Greeshma, and Raffaella, together with our international network of collaborators, on a newly published paper that came out in Nature Communications in Dec 2024, in a special collection on the Biology of rare genetic disorders. In this collaborative work, we looked at the structure of proteins behind Huntington’s disease (HD), enabled by crucial funding from the CampagneTeam Huntington and the CHDI Foundation. HD is an inherited neurodegenerative disease, with patients having a mutated form of the huntingtin (HTT) gene. The mutation affects a repeating sequence of CAG codons that has been expanded in HD patients. This translates […]
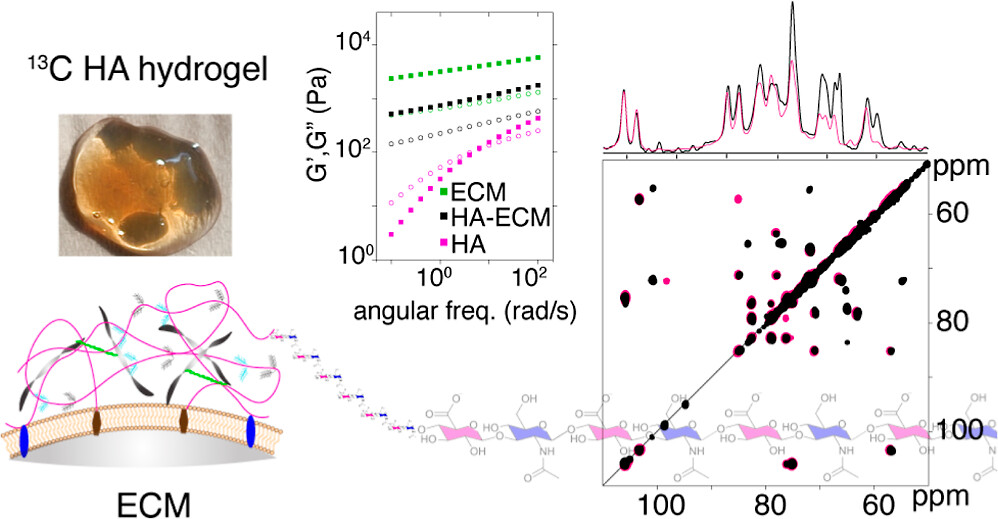
Publication: NMR of 13C-labeled hyaluronic acid hydrogels (in context of ECM)
Congratulations to PhD student Pushpa Rampratap (and her co-authors!) on the publication of a new paper on the use of solid-state NMR spectroscopy to study hydrogels that mimic aspects of the extracellular matrix (ECM). Building on her previously published approach to produce 13C labeled hyaluronic acid (HA; with very high molecular weights), she performed extensive series of magic-angle-spinning NMR analyses of HA hydrogels under various conditions. Notably, this included ECM-mimicking conditions that are commonly used in cell culture and biomedical engineering studies (using the Geltrex ECM extract). The resulting (very nice) paper shows the power of combining 13C enrichment with […]

Publication: New paper about photochemical approaches to studying polyQ protein aggregation.
Congratulations to PhD student Raffaella Parlato, Dr. Jana Volaric, and their collaborators, on the publication of a nice new paper in the Journal of the American Chemical Society. This is the final result of an idea from some years ago, which came together very nicely thanks to a great team of collaborators. The goal of this work was to explore the idea of putting polyglutamine aggregation under some degree of photo-control. In prior work, it has been shown that b-hairpin formation is a key step in the aggregation process of expanded polyQ proteins. Azobenzene-based groups can be used to favor […]

Publication: Review article on polyglutamine protein analysis by solid-state NMR spectroscopy.
Our new review article summarizing progress in polyglutamine protein studies by solid-state NMR is now available on the website of the journal Biochemical Society Transactions. This is an invited mini-review that was requested to cover the progress made in our understanding the aggregation and misfolding of mutant polyglutamine proteins implicated in diseases such as Huntington’s disease and several versions of spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA). We describe how studies from ssNMR has been used to better understand the structure of these protein aggregates, and thus helps us analyze how the aggregation process occurs and how aggregates may play a role in these […]